2. Develop for Azure storage (15-20%)
2.1 Develop solutions that use Cosmos DB storage
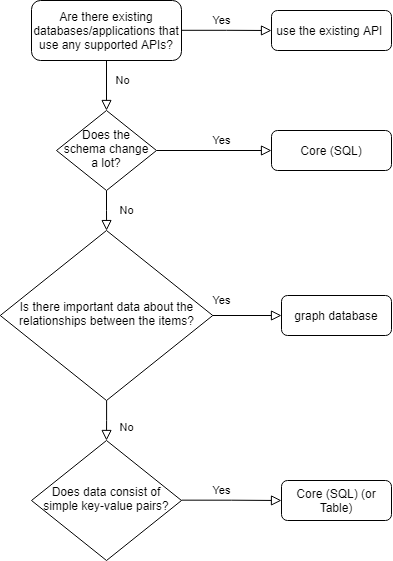
select the appropriate API and SDK for a solution
- Azure Cosmos DB
- data is stored in atom-record-sequence (ARS) format
- data is abstracted/projected as an API that is specified when creating the database
- Choices
- Consistency levels
- strong, bounded staleness, session, consistent prefix, eventual
- Multi-model
- document, key-value, wide-column, graph-based
- Data access and data manipulation
- use your own industry standard APIs
- Azure Cosmos DB account APIs
- Core (SQL)
- traditional NoSQL document store: query hierarchical JSON documents with SQL-like language
- e.g.:
SELECT, FROM, WHERE, ...
- e.g.:
- uses JavaScript’s type system, expression evaluation and function invocation
- traditional NoSQL document store: query hierarchical JSON documents with SQL-like language
- MongoDB
- supports MongoDB wire protocol: allows existing MongoDB client SDKs, drivers and tools to interact with the data
- JSON document format queries:
- e.g.:
db.Items.find({},{productName:1,_id:0})
- e.g.:
- Cassandra
- possible to query data by using Cassandra Query Language (CQL), data appears in partitioned row store
- e.g.:
CREATE KEYSPACE, CREATE TABLE, ALTER TABLE, USE, INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE...CREATE TABLE Catalog.Items(id text, productName text, description text, supplier text, quantity int, unitCost float, retailPrice float, categories map<text,text>, primary key (id));SELECT id, productName FROM catalog.items
- e.g.:
- possible to query data by using Cassandra Query Language (CQL), data appears in partitioned row store
- Azure Table
- supports applications that are written for Azure Table Storage that needs premium capabilities (global distribution, high availability, scalable throughput)
- often used for IoT data
- allows for indexing on the Partition and Row keys, no secondary indexes exist
- automatically indexes all the properties, requires no index management
- querying is accomplished by using OData and LINQ queries in code + original REST API for GET operations
- e.g.:
SELECT i.productName FROM Items i
- e.g.:
- supports applications that are written for Azure Table Storage that needs premium capabilities (global distribution, high availability, scalable throughput)
- Gremlin (graph)
- provides graph-based view over the data
- vertex: individual item in database
- edge: relationship between items in database
- traversal query language: Apache Tinkerpop - Gremlin
- e.g.: ```js # add 3 vertices (products) g.addV(‘product’).property(‘productName’, ‘Industrial Saw’).property(‘description’, ‘Cuts through anything’).property(‘quantity’, 261) g.addV(‘product’).property(‘productName’, ‘Belt Sander’).property(‘description’, ‘Smoothes rough edges’).property(‘quantity’, 312) g.addV(‘product’).property(‘productName’, ‘Cordless Drill’).property(‘description’, ‘Bores holes’).property(‘quantity’, 647)
# add 2 edges (product relationships) g.V().hasLabel(‘product’).has(‘productName’, ‘Industrial Saw’).addE(‘boughtWith’).to(g.V().hasLabel(‘product’).has(‘productName’, ‘Belt Sander’)) g.V().hasLabel(‘product’).has(‘productName’, ‘Industrial Saw’).addE(‘boughtWith’).to(g.V().hasLabel(‘product’).has(‘productName’, ‘Cordless Drill’))
# query products g.V().hasLabel(‘product’).has(‘productName’, ‘Industrial Saw’).outE(‘boughtWith’) ```
- returned results are in GraphSON format
- e.g.:
{ "id": "6c69fba7-2f76-421f-a24e-92d4b8295d67", "label": "boughtWith", "type": "edge", "inVLabel": "product", "outVLabel": "product", "inV": "faaf0997-f5d8-4d01-a527-ae29534ac234", "outV": "a9b13b8f-258f-4148-99c0-f71b30918146" }
- e.g.:
- provides graph-based view over the data
- Core (SQL)
- Consistency levels
- Decision Flow
implement partitioning schemes and partition keys
- partitioning schemes: scale individual containers in a database to meet the performance needs of your application
- logical partitions: items in a container are divided into distinct subsets
- based on the value of a partition key: associated with each item in a container, all items in a logical partition have the same partition key value
- item index = item ID + partition key
- choosing the right partition key is important for performance
- defines the scope of database transactions
- update items using a transaction with snapshot isolation
- based on the value of a partition key: associated with each item in a container, all items in a logical partition have the same partition key value
- physical partitions: container is scaled by distributing data and throughput across physical partitions
- internally, on or more logical partitions are mapped to a single physical partition
- containers have many logical partitions, but only require a single physical partition
- see container’s physical partition in Azure Portal -> Storage -> Metrics blade
- logical partitions: items in a container are divided into distinct subsets
- choosing a partition key: requirements
- should be immutable property
- have a high cardinality
- request unit (RU) consumption and data storage should be spread evenly across all logical partitions
- for large read-heavy containers: choose partition key that appears frequently as a filter in your queries -> reduces cross-partition queries
- for small read/write-heavy containers: use item ID as partition key
perform operations on data and Cosmos DB containers
- Data Explorer: Azure Portal -> Databases -> Azure Cosmos DB -> select database -> Data Explorer
- Add new items
- Query/filter data using:
- SQL queries
- Geospatial queries (GeoJSON points - coordinates)
- stored procedures
- perform complex transactions on documents and properties
- written in JavaScript, stored in container on Azure Cosmos DB
- improves performance over client-side programming
- only way to achieve atomic transactions within Azure Cosmos DB
- client-side SDKs do not support transactions
- e.g.:
function helloWorld() { var context = getContext(); var response = context.getResponse(); response.setBody("Hello, World"); }
- user-defined functions (UDF)
- extend Azure Cosmos DB SQL query language grammar
- implement custom business login, such as calculation on properties/documents
- can only be called from inside queries (unlike stored procedures), they do not have access to the context object
- e.g.:
function producttax(price) { if (price == undefined) throw 'no input'; var amount = parseFloat(price); if (amount < 1000) return amount * 0.1; else if (amount < 10000) return amount * 0.2; else return amount * 0.4; }
set the appropriate consistency level for operations
- Consistency levels:
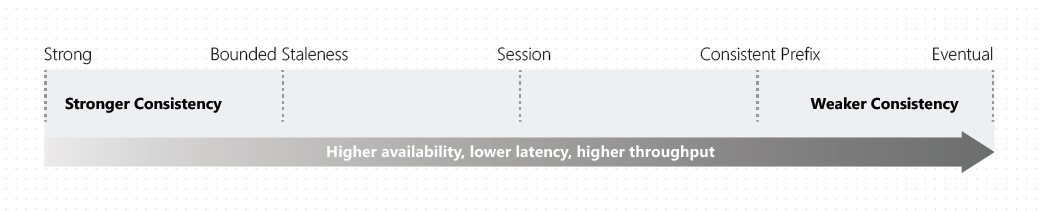
- Strong consistency
- linearizability guarantee: reads are guaranteed to return most recent committed version of an item, client never sees uncommitted or partial write

- Bounded staleness:
- consistent-prefix guarantee: reads might lag behind writes by “K” versions or by “T” time interval
- staleness can be configured in 2 ways:
- number of versions (K) of the item - 100 items
- time interval (T) reads might lag behind writes - 5 seconds
- staleness can be configured in 2 ways:
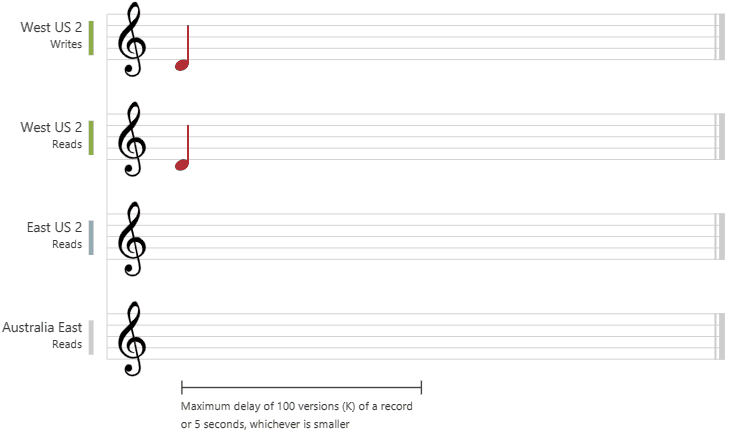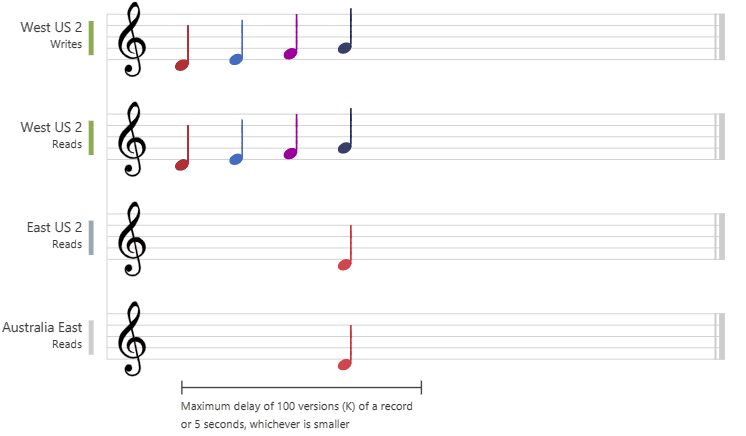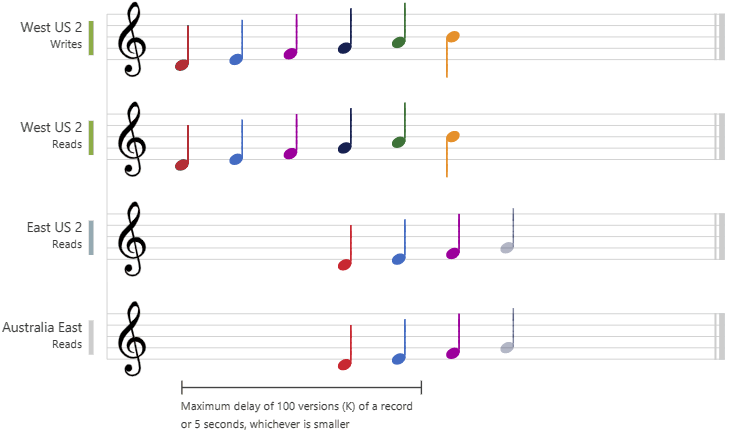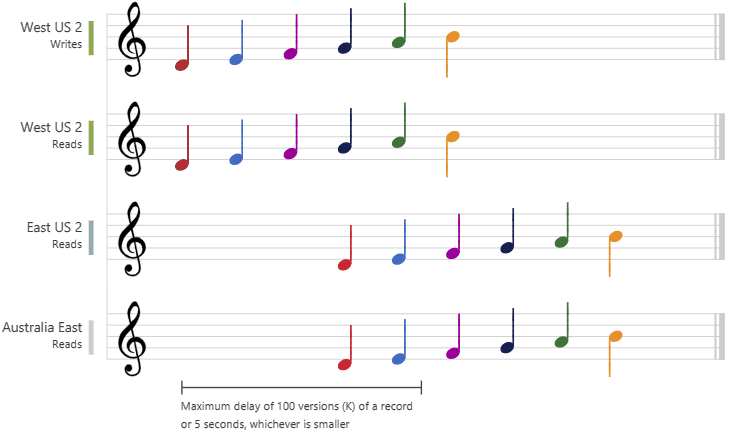
- consistent-prefix guarantee: reads might lag behind writes by “K” versions or by “T” time interval
- Session
- within a single client session reads are guaranteed to honor the:
- consistent-prefix guarantees
- monotonic reads/writes guarantees
- read-your-writes guarantees
- write-follows-reads guarantees
- assumes a single “writer” session or sharing the session token for multiple writers

- within a single client session reads are guaranteed to honor the:
- Consistent prefix
- updates that are returned contain some prefix of all the updates, with no gaps

- Eventual
- no ordering guarantee for reads
- in absence of further writes, the replicas eventually converge

- Strong consistency
manage change feed notifications
- persistent record of changes to a container in the order they occur
- works by listening to an Azure Cosmos container for any changes
- outputs the sorted list of documents that were changed in the order in which they were modified
- persisted changes can be processed asynchronously and incrementally
- output can be distributed across on or more consumers for parallel processing
- working with change feed
- with Azure Functions: create small reactive Azure Functions that will automatically be triggered on each new event in change feed
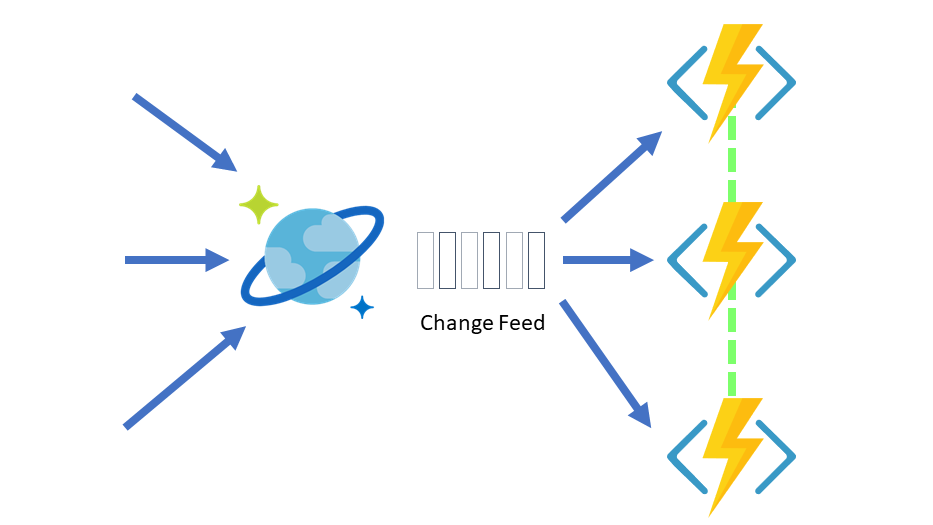
- with change feed processor: simplifies the process of reading the change feed and distribute the event processing across multiple consumers effectively
- components:
- monitored container: has the data from which the change feed is generated
- lease container: acts as a state storage and coordinates processing across multiple workers
- host: application instance that uses the change feed processor to listen for changes, multiple instances with the same lease configuration can run in parallel
- delegate: code that defines what you want to do with each batch of changes that the change feed processor reads
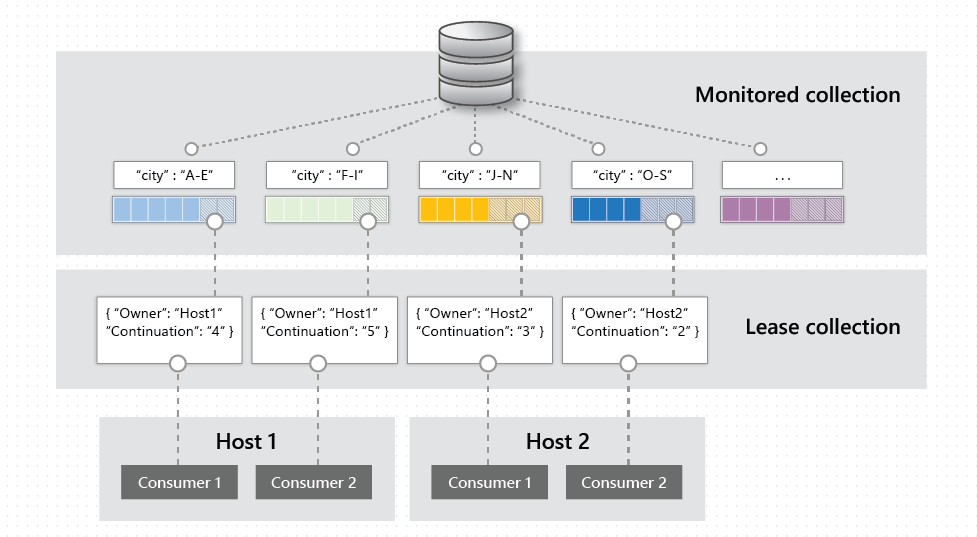
- implementation:
- from monitored container
Container(= code entrypoint), callGetChangeFeedProcessorBuilder - e.g.:
/// <summary> /// Start the Change Feed Processor to listen for changes and process them with the HandleChangesAsync implementation. /// </summary> private static async Task<ChangeFeedProcessor> StartChangeFeedProcessorAsync( CosmosClient cosmosClient, IConfiguration configuration) { string databaseName = configuration["SourceDatabaseName"]; string sourceContainerName = configuration["SourceContainerName"]; string leaseContainerName = configuration["LeasesContainerName"]; Container leaseContainer = cosmosClient.GetContainer(databaseName, leaseContainerName); ChangeFeedProcessor changeFeedProcessor = cosmosClient.GetContainer(databaseName, sourceContainerName) .GetChangeFeedProcessorBuilder<ToDoItem>(processorName: "changeFeedSample", onChangesDelegate: HandleChangesAsync) .WithInstanceName("consoleHost") .WithLeaseContainer(leaseContainer) .Build(); Console.WriteLine("Starting Change Feed Processor..."); await changeFeedProcessor.StartAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Change Feed Processor started."); return changeFeedProcessor; }
- from monitored container
- components:
- with Azure Functions: create small reactive Azure Functions that will automatically be triggered on each new event in change feed
2.2 Develop solutions that use blob storage
move items in Blob storage between storage accounts or containers
- synchronous and asynchronous methods for transferring blobs
- move blobs between Azure storage accounts using:
- .NET Storage Client library
- collection of objects/methods that you can use to build custom applications that manipulate items held in Azure Storage
- construct your own applications to upload/download/migrate blobs between storage accounts
- incorporate your code into existing applications, deploy code to variety of environments (e.g.: Azure Functions) ```csharp using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage; using Microsoft.WindowsAzure.Storage.Blob;
// The variable sourceConnection is a string holding the connection string for the storage account CloudStorageAccount sourceAccount = CloudStorageAccount.Parse(sourceConnection); CloudBlobClient sourceClient = sourceAccount.CreateCloudBlobClient();
// Download a blob CloudBlobContainer sourceBlobContainer = sourceClient.GetContainerReference(sourceContainer); ICloudBlob sourceBlob = await sourceBlobContainer.GetBlobReferenceFromServerAsync(“MyBlob.doc”); Console.WriteLine($”Last modified: {sourceBlob.Properties.LastModified}”); await sourceBlob.DownloadToFileAsync(“MyFile.doc”, System.IO.FileMode.Create);
// Upload a blob CloudBlobContainer destBlobContainer = destClient.GetContainerReference(destContainer); CloudBlockBlob destBlob = destBlobContainer.GetBlockBlobReference(“NewBlob.doc”); await destBlob.UploadFromFileAsync(“MyFile.doc”);
// Delete a blob bool blobExisted = await sourceBlob.DeleteIfExistsAsync();
// Iterate blobs in a container BlobContinuationToken token = null;
do { BlobResultSegment segment = await blobContainer.ListBlobsSegmentedAsync(prefix: “”, currentToken: token); foreach (CloudBlockBlob blobItem in segment.Results) { // Process the current blob ICloudBlob blob = await blobContainer.GetBlobReferenceFromServerAsync(blobItem.Name); … } } while (token != null);
```csharp // Copy blob between storage accounts CloudBlockBlob destBlob = destContainer.GetBlockBlobReference(sourceBlob.Name); await destBlob.StartCopyAsync(new Uri(GetSharedAccessUri(sourceBlob.Name, sourceContainer))); // Create a SAS token for the source blob, to enable it to be read by the StartCopyAsync method private static string GetSharedAccessUri(string blobName, CloudBlobContainer container) { DateTime toDateTime = DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(60); SharedAccessBlobPolicy policy = new SharedAccessBlobPolicy { Permissions = SharedAccessBlobPermissions.Read, SharedAccessStartTime = null, SharedAccessExpiryTime = new DateTimeOffset(toDateTime) }; CloudBlockBlob blob = container.GetBlockBlobReference(blobName); string sas = blob.GetSharedAccessSignature(policy); return blob.Uri.AbsoluteUri + sas; } - Azure CLI:
az storage- upload/download blobs between blob storage/local file system
az storage blob copyaz storage blob upload-batch \ --destination specifications \ --pattern "*.md" \ --source ~/sample/specifications \ --account-name $HOT_STORAGE_NAME \ --account-key $HOT_KEY
- runs asynchronously
- uses Azure Storage service to manage the copy process
- upload/download blobs between blob storage/local file system
- AzCopy tool
- transfer data in/out/between Azure storage accounts
- upload data:
azcopy copy "myfile.txt" "https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer/" - download data:
azcopy copy "https://myaccount.blob.core.windows.net/mycontainer/myblob?<sas token>" "myblobdata" - between storage acounts:
azcopy copy "https://sourceaccount.blob.core.windows.net/sourcecontainer/*?<source sas token>" "https://destaccount.blob.core.windows.net/destcontainer/*?<dest sas token>"
- upload data:
- supports hierarchical containers
- supports selection by pattern matching
- transfer data in/out/between Azure storage accounts
- .NET Storage Client library
set and retrieve properties and metadata
- Set/retrieve system properties: Azure Storage client library for .NET
- exist on each Blob storage resource, some correspond to certain standard HTTP headers
- e.g.: set
ContentTypeadnContentLanguagesystem properties using theSetHttpHeadersorSetHttpHeadersAsynccallspublic static async Task SetBlobPropertiesAsync(BlobClient blob) { Console.WriteLine("Setting blob properties..."); try { // Get the existing properties BlobProperties properties = await blob.GetPropertiesAsync(); BlobHttpHeaders headers = new BlobHttpHeaders { // Set the MIME ContentType every time the properties // are updated or the field will be cleared ContentType = "text/plain", ContentLanguage = "en-us", // Populate remaining headers with // the pre-existing properties CacheControl = properties.CacheControl, ContentDisposition = properties.ContentDisposition, ContentEncoding = properties.ContentEncoding, ContentHash = properties.ContentHash }; // Set the blob's properties. await blob.SetHttpHeadersAsync(headers); } catch (RequestFailedException e) { Console.WriteLine($"HTTP error code {e.Status}: {e.ErrorCode}"); Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Console.ReadLine(); } }
- Set/retrieve user-defined metadata
- name-value pairs in the
Metadatacollection on the resource - set using:
SetMetadataandSetMetadataAsync- e.g.:
public static async Task AddBlobMetadataAsync(BlobClient blob) { Console.WriteLine("Adding blob metadata..."); try { IDictionary<string, string> metadata = new Dictionary<string, string>(); // Add metadata to the dictionary by calling the Add method metadata.Add("docType", "textDocuments"); // Add metadata to the dictionary by using key/value syntax metadata["category"] = "guidance"; // Set the blob's metadata. await blob.SetMetadataAsync(metadata); } catch (RequestFailedException e) { Console.WriteLine($"HTTP error code {e.Status}: {e.ErrorCode}"); Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Console.ReadLine(); } }
- e.g.:
- get using:
GetPropertiesandGetPropertiesAsync- e.g.:
public static async Task ReadBlobMetadataAsync(BlobClient blob) { try { // Get the blob's properties and metadata. BlobProperties properties = await blob.GetPropertiesAsync(); Console.WriteLine("Blob metadata:"); // Enumerate the blob's metadata. foreach (var metadataItem in properties.Metadata) { Console.WriteLine($"\tKey: {metadataItem.Key}"); Console.WriteLine($"\tValue: {metadataItem.Value}"); } } catch (RequestFailedException e) { Console.WriteLine($"HTTP error code {e.Status}: {e.ErrorCode}"); Console.WriteLine(e.Message); Console.ReadLine(); } }perform operations on data by using the appropriate SDK
- e.g.:
- name-value pairs in the
- Azure Blob Storage client library v12 for .NET:
Azure.storage.Blobs- Upload blobs
await blobClient.UploadAsync(localFilePath, true); - List blobs
await foreach (BlobItem blobItem in containerClient.GetBlobsAsync()) { Console.WriteLine("\t" + blobItem.Name); } - Download blobs
await blobClient.DownloadToAsync(downloadFilePath);
- Upload blobs
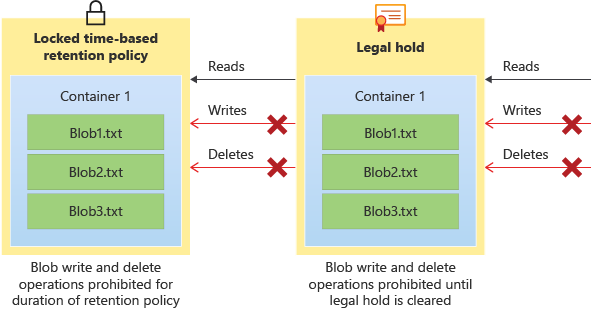
implement storage policies, and data archiving and retention
- Data archiving and retention policies:
- all blobs in the container will stay in the immutable state for the duration of the effective retention period
- Configure: Azure Portal -> Azure Time Series Insights environment
- Settings -> Storage configuration
- Data retention time (in days)
- Capacity
- Storage limit exceeded behavior
- Purge old data
- Pause ingress
- Settings -> Storage configuration