1. Cloud Concepts (20-25%)
1.1 Benefits & Considerations of using cloud services
Reasons to switch to the cloud
- lower operating costs
- run infrastructure more efficiently
- scale as your business needs change
- deliver new features at higher speeds
- limitless pool of raw compute/storage/networking components
- speech recognition + other cognitive services to help make your application stand out
- analytics services that deliver telemetry data from software/devices
Benefits of cloud computing
- High availability: Depending on the service-level agreement (SLA) that you choose, your cloud-based apps can provide a continuous user experience with no apparent downtime, even when things go wrong
- Scalability: Apps in the cloud can scale vertically and horizontally:
- scale vertically to increase compute capacity by adding RAM or CPUs to a virtual machine
- scaling horizontally increases compute capacity by adding instances of resources, such as adding VMs to the configuration
- Elasticity: You can configure cloud-based apps to take advantage of autoscaling, so your apps always have the resources they need
- Agility: Deploy and configure cloud-based resources quickly as your app requirements change
- Geo-distribution: You can deploy apps and data to regional datacenters around the globe, thereby ensuring that your customers always have the best performance in their region
- Disaster recovery: By taking advantage of cloud-based backup services, data replication, and geo-distribution, you can deploy your apps with the confidence that comes from knowing that your data is safe in the event of disaster
Capital Expenditure (CapEx) vs. Operational Expenditure (OpEx)
- Capital Expenditure (CapEx): is the up-front spending of money on physical infrastructure, and then deducting that up-front expense over time. The up-front cost from CapEx has a value that reduces over time
- Operational Expenditure (OpEx) is spending money on services or products now, and being billed for them now. You can deduct this expense in the same year you spend it
- no up-front cost, as you pay for a service or product as you use it
Consumption-based model
- no upfront costs
- no need to purchase and manage costly infrastructure that users might not use to its fullest
- ability to pay for additional resources when they are needed
- ability to stop paying for resources that are no longer needed
1.2 Categories of cloud services
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
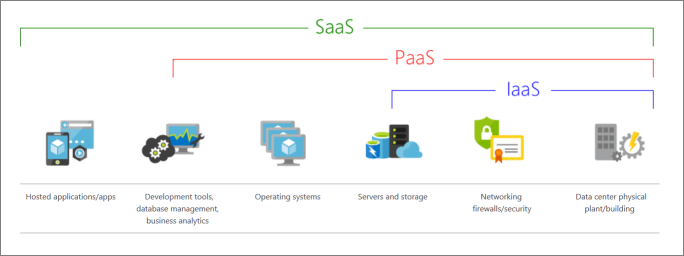
Exam: identify cloud service type based on a specific use case
Shared responsibility model

Serverless computing
- Serverless computing: enables developers to build applications faster by eliminating the need for them to manage infrastructure
- serverless applications, the cloud service provider automatically provisions, scales, and manages the infrastructure required to run the code
- serverless architectures are highly scalable and event-driven, only using resources when a specific function or trigger occurs
1.3 Types of cloud computing
Definition: Public, Private, Hybrid cloud
- Public cloud
- services are offered over the public internet and available to anyone who wants to purchase them
- cloud resources (servers, storage) are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider, and delivered over the internet
- Private cloud
- private cloud consists of computing resources used exclusively by users from one business or organization
- private cloud can be physically located at your organization’s on-site (on-premises) datacenter, or it can be hosted by a third-party service provider
- Hybrid cloud
- hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines a public cloud and a private cloud by allowing data and applications to be shared between them
Comparison
- Public cloud
- No capital expenditures to scale up
- Applications can be quickly provisioned and deprovisioned
- Organizations pay only for what they use
- Private cloud
- Hardware must be purchased for start-up and maintenance
- Organizations have complete control over resources and security
- Organizations are responsible for hardware maintenance and updates
- Hybrid cloud
- Provides the most flexibility
- Organizations determine where to run their applications
- Organizations control security, compliance, or legal requirements