2. Cloud Azure Services (15-20%)
2.1 Core Azure Services
Regions and Region Pairs, Availability Zones
- Azure Regions: geographical area on the planet that contains 1+ datacenters that are networked together with a low-latency network
- Azure assigns/controls the resources within each region to ensure workloads are balanced
- some services or VM features are only available in certain regions
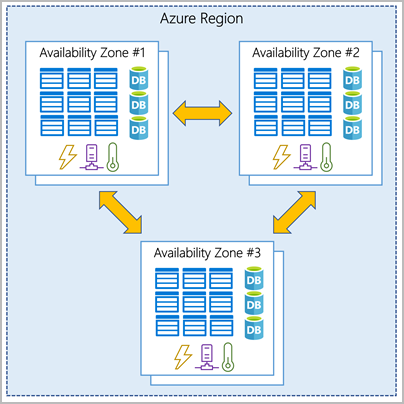
- Azure Availability Zones: physically separate datacenters within an Azure region made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking
- isolation boundary to ensure high availability
- availability zones are connected through high-speed, private fiber-optic networks
- usage
- zonal services: pin resource to specific zone (VMs, managed disks, IP addresses)
- zone-redundant services: platform replicates automatically across zones (zone-redundant storage, SQL database)
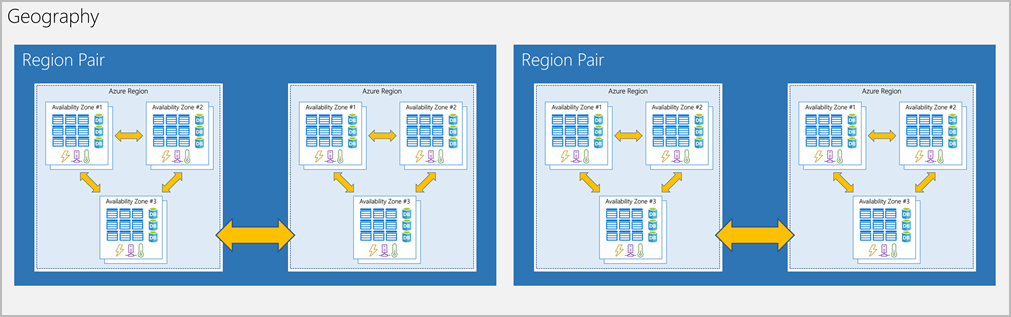
- Azure Region Pair: each region is paired with another region within the same geography (such as US, Europe, or Asia)
- allows for the replication of resources across a geography that helps reduce the likelihood of interruptions because of events such as natural disasters, civil unrest, power outages, or physical network outages
- example: US west + US east region pair
Subscriptions, Management Groups, Resource Groups, Resources
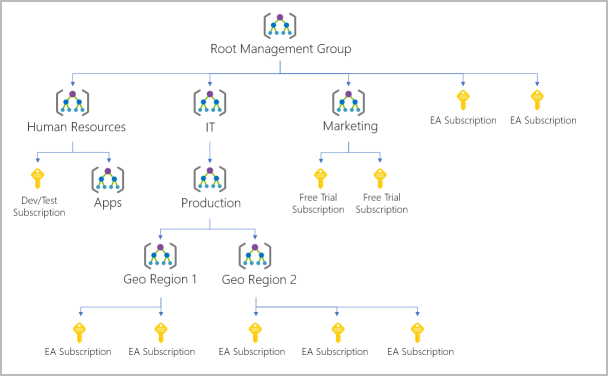
- Azure account scope levels: top-down hierarchy of an organization structure in Azure
- Resources: instances of services (VMs, storage, DBs)
- Resource groups: logical containers for combined resources
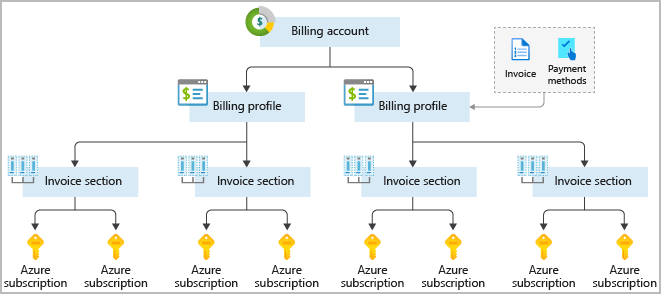
- Subscriptions: groups together user accounts and resources that have been created by those user accounts
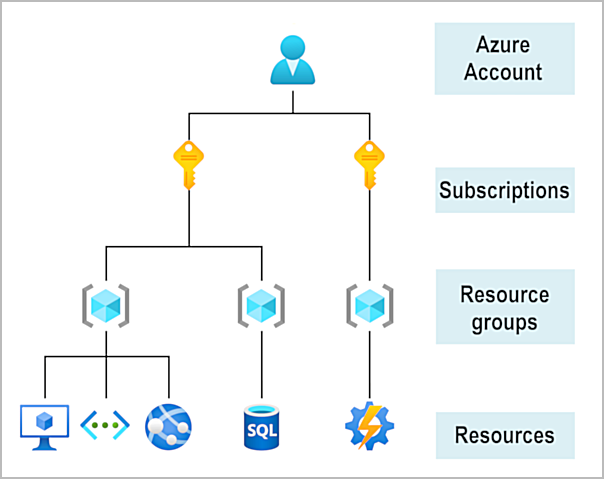
- billing boundary: set limits/quotas on resources
- access control boundary: access-management policies at the subscription level
- create separate subscriptions to reflect different organizational structures:
- environments: development, testing, security, …
- organizational structures: different teams, departments, projects, …
- billing: costs are aggregated at subscription level
- subscription limits: in case the max number of Azure resources within subscription is exceeded
- Management groups: manage access/policy/compliance for multiple subscriptions
Azure Resource Manager
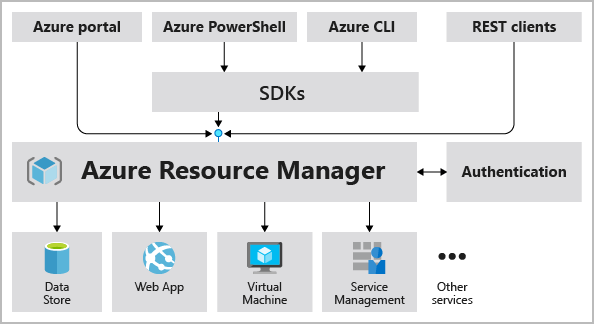
- Azure Resource Manager: deployment and management service for Azure
- manage infrastructure through declarative templates rather than scripts
- ARM templates: JSON file that defines what you want to deploy to Azure
- deploy/manage/monitor all resources as a group, rather than handling these resources individually
- redeploy solutions throughout the development life cycle in a consistent state
- define dependencies between resources to deploy in the correct order
- apply access control to all services using RBAC
- apply tags to resources to logically organize resources within subscriptions
- view costs for a group of resources that share the same tag
2.2 Core resources available in Azure
Compute
- Azure Virtual Machines: create and use VMs in the cloud
- IaaS: total control over an operating system and environment
- ability to run custom software
- use custom hosting configurations
- Virtual machine scale sets: use to deploy and manage a set of identical VMs
- Azure Batch: enables large-scale parallel and high-performance computing (HPC) batch jobs with the ability to scale to 1000+ VMs
- Azure App Services: quickly build, deploy, and scale enterprise-grade web, mobile, and API apps running on any platform
- WebJobs: used to run background tasks as part of your application logic
- deployment and management are integrated into the platform
- endpoints can be secured
- sites can be scaled quickly to handle high traffic loads
- built-in load balancing and traffic manager provide high availability
- Azure Container Instances (ACI): run multiple instances of a containerized application on a single host machine
- PaaS: allows you to upload your containers, which it runs for you
- Containers: lightweight, virtualized application environments
- Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS): used to deploy solutions using a microservice architecture
- complete orchestration (automating, managing, and interacting with a large number of containers) service for containers with distributed architectures
- scale the back end separately to improve performance
- decide to use a different storage service
- replace the storage container without affecting the rest of the application
- Azure Functions: commonly used when you need to perform work in response to an event
- Abstraction of servers
- Event-driven scale
- Micro-billing
- Azure Logic Apps: web-based designer and can execute logic triggered by Azure services without writing any code
- Windows Virtual Desktop: desktop and application virtualization service that runs on the cloud
- enables your users to use a cloud-hosted version of Windows from any location
Networking
- Virtual Networks
- Isolation and segmentation
- Internet communications
- Communicate between Azure resources
- Virtual networks
- Service endpoints
- Communicate with on-premises resources
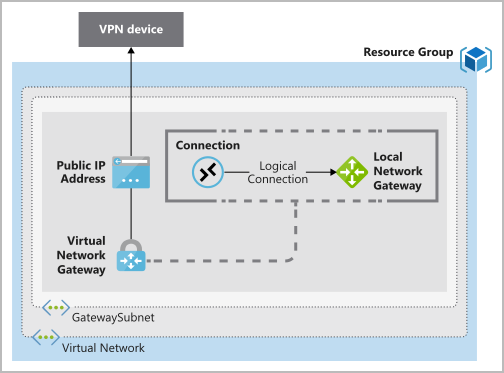
- Point-to-site virtual private networks: connection from a computer outside your organization, back into your corporate network
- Site-to-site virtual private networks: links your on-premises VPN device or gateway to the Azure VPN gateway in a virtual network
- Azure ExpressRoute: private connection from your on-premises infrastructure to your Azure infrastructure with greater bandwidth, redundancy and higher levels of security
- Not encrypted: data doesn’t travel over the public internet, so it’s not exposed to the potential risks associated with internet communications
- L3 connectivity
- Built-in redundancy
- Connectivity to Microsoft services
- Across on-premises connectivity with ExpressRoute Global Reach
- Dynamic Routing
- ExpressRoute connectivity models
- CloudExchange colocation: Colocated providers offer both L2 and L3 connections between your infrastructure, which might be located in the colocation facility, and the Microsoft cloud
- Point-to-point Ethernet connection: L2 and L3 connectivity between your on-premises site and Azure
- Any-to-any connection: integrate your WAN with Azure by providing connections to your offices and datacenters, all WAN providers offer L3 connectivity
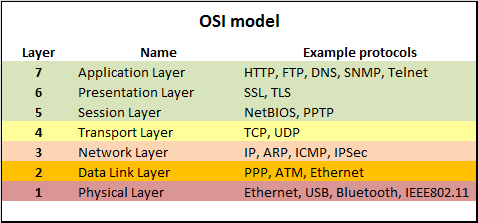
- Info: OSI model layers
- Route network traffic
- Routing tables
- Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for routing between autonomous systems (AS)
- Filter network traffic
- Network security groups (NSG): Azure resource that can contain multiple inbound and outbound security rules
- Network virtual appliances: specialized VM that can be compared to a hardened network appliance (running a firewall or performing WAN optimization)
- Connect virtual networks
- Virtual network peering: enables resources in each virtual network to communicate with each other
- virtual networks can be in separate regions, which allows you to create a global interconnected network through Azure
- User-Defined Routing (UDR): allows network admins to control the routing tables between subnets within a VNet, as well as between VNets
- allows greater control over network traffic flow
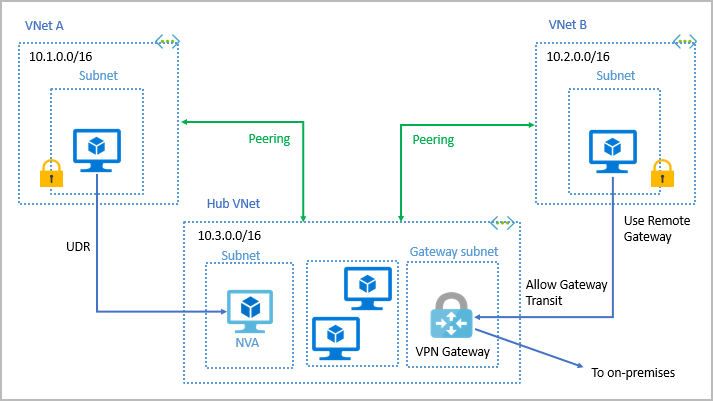
- VPN Gateway
- Connect on-premises datacenters to virtual networks through a site-to-site connection
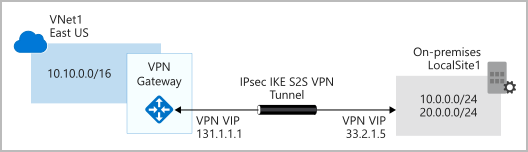
- policy-based: specify statically the IP address of packets that should be encrypted through each tunnel
- route-based: IPSec tunnels are modeled as a network interface or virtual tunnel interface
- IP routing (static/dynamic routes/routing protocols) decides which one of these tunnel interfaces to use when sending each packet
- Connect individual devices to virtual networks through a point-to-site connection
- Connect virtual networks to other virtual networks through a network-to-network connection
- Deployment resource requirements:
- High-availability strategies
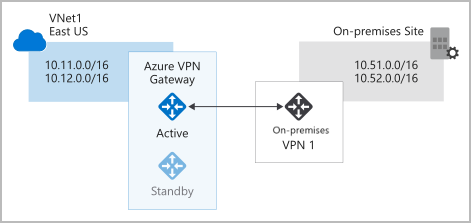
- Active/standby configuration: when planned maintenance or unplanned disruption affects the active instance, the standby instance automatically assumes responsibility for connections without any user intervention
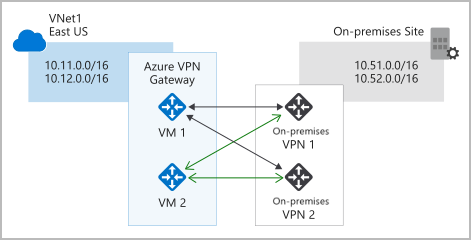
- Active/active configuration: assign a unique public IP address to each instance, create separate tunnels from the on-premises device to each IP address
Storage
- Storage Accounts: provides a unique namespace for your Azure Storage data, that’s accessible from anywhere in the world over HTTP or HTTPS
- data in this account is secure, highly available, durable and scalable
- Container (Blob) Storage: object storage solution for the cloud, store massive amounts of data, such as text or binary data
- use cases
- Serving images or documents directly to a browser
- Storing files for distributed access
- Streaming video and audio
- Storing data for backup and restore, disaster recovery, and archiving
- Storing data for analysis by an on-premises or Azure-hosted service
- Storing up to 8 TB of data for virtual machines
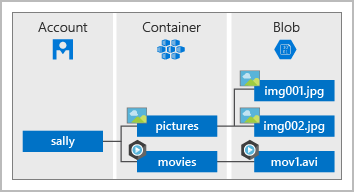
- Access tiers
- Hot access tier: optimized for storing data that is accessed frequently (for example, images for your website)
- Cool access tier: optimized for data that is infrequently accessed and stored for 30+
- Archive access tier: appropriate for data that is rarely accessed and stored for 180+, with flexible latency requirements
- Disk Storage: provides disks for Azure virtual machines
- allows data to be persistently stored and accessed from an attached virtual hard disk
- File Storage: fully managed file shares in the cloud that are accessible via the industry standard Server Message Block and Network File System
- can be mounted concurrently by cloud or on-premises deployments of Windows, Linux, and macOS
- applications running in Azure virtual machines or cloud services can mount a file storage share to access file data (~SMB)
- you can access the files from anywhere in the world, by using a URL that points to the file
- Shared Access Signature (SAS) tokens allow access to a private asset for a specific amount of time
Database
- Cosmos DB: globally distributed, multi-model database service
- elastically and independently scale throughput and storage across any number of Azure regions worldwide
- take advantage of fast, single-digit-millisecond data access by using any one of several popular APIs
- provides comprehensive service level agreements for throughput, latency, availability, and consistency guarantees
- supports schema-less data
- Azure SQL Database: relational database based on the latest stable version of the Microsoft SQL Server database engine
- PaaS database engine
- fully managed service that has built-in high availability, backups, and other common maintenance operations
- handles most of the database management functions, such as upgrading, patching, backups, and monitoring, without user involvement
- enables you to process both relational data and non-relational structures
- graphs, JSON, spatial, and XML
- advanced query processing features
- high-performance, in-memory technologies and intelligent query processing
- Azure Database for MySQL: relational database service based on the MySQL Community Edition database engine
- built-in high availability with no additional cost
- predictable performance and inclusive, pay-as-you-go pricing
- scale as needed, within seconds
- ability to protect sensitive data at-rest and in-motion
- automatic backups
- enterprise-grade security and compliance
- Azure Database for PostgreSQL: relational database service based on the community version of the open-source PostgreSQL database engine
- Deployment options
- Single server
- Hyperscale (Citus)
- supports multi-tenant applications
- queries across multiple machines by using sharding
- SQL Managed Instance: scalable cloud data service that provides the broadest SQL Server database engine compatibility with all the benefits of a fully managed platform as a service
Analytics
- Azure Synapse Analytics: limitless analytics service that brings together enterprise data warehousing and big data analytics
- query data on your terms by using either serverless or provisioned resources at scale
- unified experience to ingest, prepare, manage, and serve data for immediate BI and machine learning needs
- Azure HDInsight: fully managed, open-source analytics service for enterprises
- run popular open-source frameworks and create cluster types such as Apache Spark, Apache Hadoop, Apache Kafka, Apache HBase, Apache Storm, and Machine Learning Services
- supports a broad range of scenarios such as extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL), data warehousing
- Azure Databricks: unlock insights from all your data and build artificial intelligence solutions
- set up Apache Spark environment, autoscale and collaborate on shared projects in an interactive workspace
- supports Python, Scala, R, Java, and SQL
- supports data science frameworks/libraries: TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn
- Azure Data Lake Analytics: on-demand analytics job service that simplifies big data
- handle jobs of any scale instantly by setting the dial for how much power you need
- pay for your job when it’s running, making it more cost-effective
Azure Marketplace